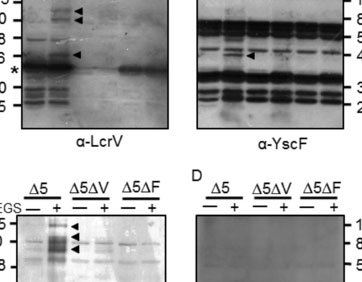
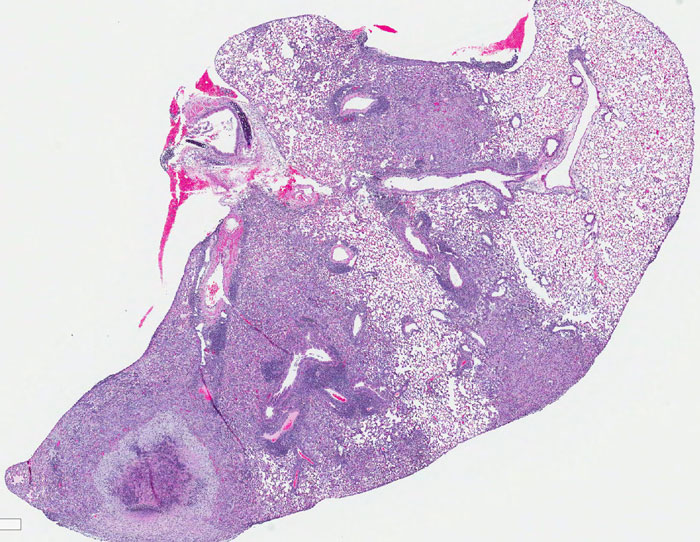
Community behavior and spatial regulation of Yersinia during microcolony formation in deep tissue sites
January, 2015
Abstract
Bacterial pathogens express virulence-specific transcriptional programs that allow tissue colonization. Although phenotypic variation has been noted in the context of antibiotic exposure, no direct evidence exists for heterogeneity in virulence-specific transcriptional programs within tissues. In a mouse model of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection, we show that at least three subpopulations of bacteria develop within a single tissue site in response to distinct host signals. Bacteria growing on the exterior of spleen microcolonies responded to soluble signals and induced the nitric oxide (NO)-detoxifying gene, hmp. Hmp effectively eliminated NO diffusion and protected the interior bacterial population from exposure to NO-derived inducing signals. A third subpopulation, constituting the most peripherally localized bacteria, directly contacted neutrophils and transcriptionally upregulated a virulence factor. These studies demonstrate that growth within tissues results in transcriptional specialization within a single focus of microbial replication, facilitating directed pathogen counterattack against the host response.